Ban Xia (Fa-True)
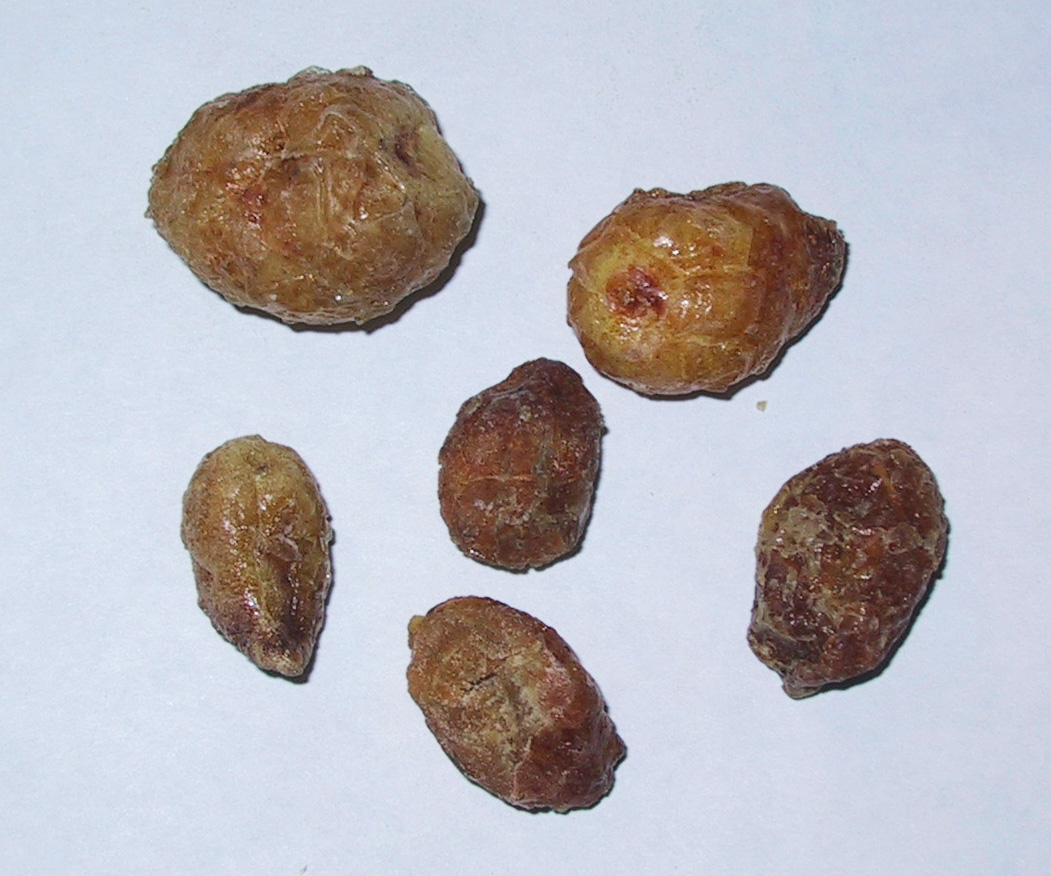

Ban Xia (Fa-True)
| SKU | AN136 | |
| Brand | Asia Naturals Raw Herbs | |
| Unit Size | 1 pound | |
| Dosage | 3 - 9 grams | |
| Taste | Acrid | |
| Properties | Warm | |
| Contraindications | Dry cough from Yin Deficiency; Sore Throat from fire excess; Bleeding | |
| Chinese Symptomology | Cold Phlegm in the Lungs; Spleen Dampness; Phlegm due to cold; Phlegm due to Stomach Deficiency; Phlegm Nodules; Phlegm Obstruction | |
| Western Symptomology | Cough with copious sputum; Nausea; Vomiting; Nodules; Goiter; Scofula; Chest Distention; Epigastric Distention | |
| Actions | Dries Dampness; Transforms Phlegm; Directs rebellious Qi downward and stops Vomiting; Dissipates Nodules and Reduces Clumps | |
| Branch | Lung; Spleen; Stomach | |
| Recommendations | Product will ship FedEx Ground, even if Expedited is selected. Call for expedited shipping rates. |
|
| Chinese name | Ban Xia (Fa-True) | |
| English name | Prepared Pinellia Tuber | |
| Description | Pinellia Rhizoma preparatum (zhi ban xia) is acrid, warm, and toxic if untreated, and enters the Spleen and Stomach channels. It is especially dispersing and drying, and because it is slippery and directs rebellious qi downward, it restores the normal descent of Stomach qi when it is rebelling upward. It eliminates water and dampness, both by drying and by dispersing; and through its ability to direct qi downward, it harmonizes the Stomach and stops nausea, hiccough, and a sensation of fullness in the hypochondrium. This Pinellia Rhizoma perparatum (zhi ban xia) is most often used for treating Spleen dampness producing profuse, clear, thin sputum with cough, or phlegm and dampness rising upward causing palpitations, insomnia, vertigo, and loss of mental clarity, or the previously mentioned Stomach symptoms. Because of its efficacy in directing rebellious qi downward and transforming phlegm, it is often combined with other substances for treating cough and dyspnea from phlegm-dampness and heat, or nausea from Stomach heat or weakness, morning sickness, and phlegm-dampness entering the collaterals and causing nodes of phlegm. (from Chinese Herbal Materia Medica, 3rd ed by Bensky) |
|